ManhattanFanout
- class ipkiss3.all.ManhattanFanout
Create L-bend-like routes that fanout all the start ports to evenly spaced outputs. To be used with a bundle connector.
- Parameters:
- end_position: ( Coord2 ), optional, *None allowed*
The coordinate where the reference route ends. If None, the fanout is made as compact as possible.This parameter is used as an ‘anchor’ to start the Manhattan bundle route
- reference: optional, *None allowed*
Port (instance:port identifier or an actual i3.Port) to align the fanout with. If None, the center of the inputs is used as reference.
- output_direction: optional
Direction of the output waveguides. Should be EAST, WEST, NORTH or SOUTH.Defaults to DIRECTION.EAST.
See also
Examples
Use output_direction to control the direction of the waveguides:
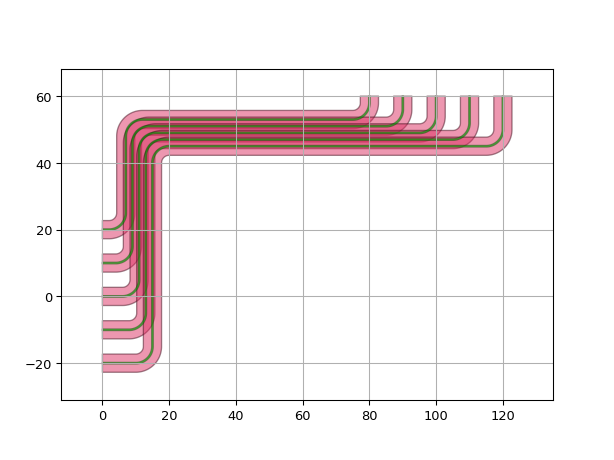
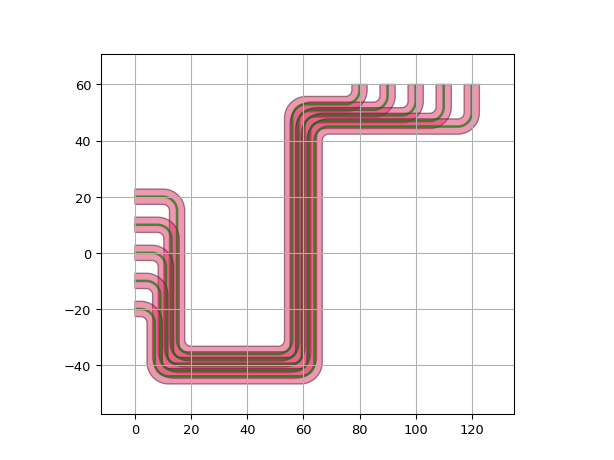
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa import ipkiss3.all as i3 start_ports = [ i3.OpticalPort(name=f"start_port_{i}", position=(0.0, -20.0 + 10 * i), angle=0) for i in range(5) ] end_ports = [i3.OpticalPort(name=f"end_port_{i}", position=(120 - 10 * i, 60), angle=-90) for i in range(5)] circuit = i3.Circuit( specs=[ i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=list(zip(start_ports, end_ports)), start_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout( # Route start_fanout to NORTH output_direction=i3.NORTH, ), end_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout( # Route end_fanout to WEST output_direction=i3.WEST, ), ) ] ) lv = circuit.Layout() lv.visualize() circuit = i3.Circuit( specs=[ i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=list(zip(start_ports, end_ports)), start_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout( # Route start_fanout to SOUTH output_direction=i3.SOUTH, ), end_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout( # Route end_fanout to WEST output_direction=i3.WEST, ), ) ] ) lv = circuit.Layout() lv.visualize()
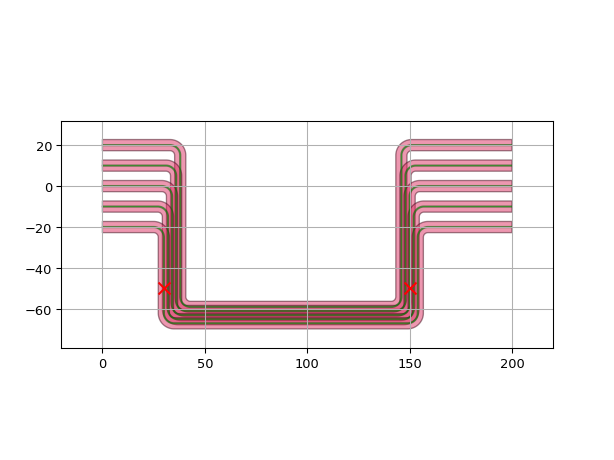
Use actual i3.Port as reference and end_position to control the alignment of the fanout:
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import ipkiss3.all as i3 start_ports = [ i3.OpticalPort(name=f"start_port_{i}", position=(0.0, -20.0 + 10 * i), angle=0) for i in range(5) ] end_ports = [ i3.OpticalPort(name=f"end_port_{i}", position=(200.0, -20.0 + 10 * i), angle=180) for i in range(5) ] circuit = i3.Circuit( specs=[ i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=list(zip(start_ports, end_ports)), start_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout( # Route start_fanout to SOUTH output_direction=i3.SOUTH, # Route the first start port to (30, -50) reference=start_ports[0], end_position=(30, -50), ), end_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout( # Route end_fanout to SOUTH output_direction=i3.SOUTH, # Route the center of the inputs to (150, -50) end_position=(150, -50), ), ) ] ) lv = circuit.Layout() lv.visualize(show=False) plt.scatter( 30, -50, marker="x", color="r", s=80, zorder=50 ) # end_position for the reference of the start_fanout plt.scatter( 150, -50, marker="x", color="r", s=80, zorder=50 ) # end_position for the reference of the end_fanout plt.show()
Use ‘instance:port’ as reference and end_position to control the alignment of the fanout:
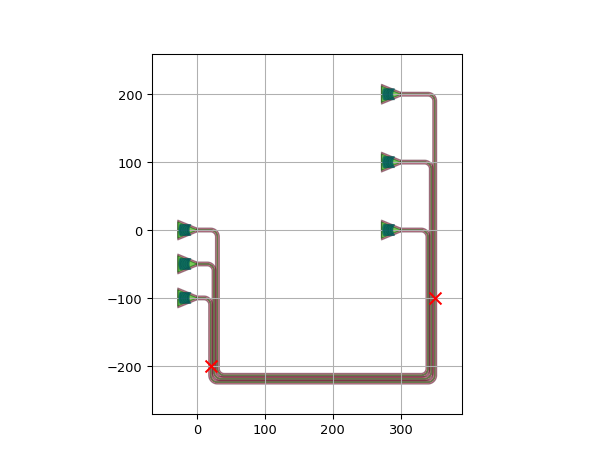
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating import ipkiss3.all as i3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fc = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating() circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={ "fc1": fc, "fc2": fc, "fc3": fc, "fc4": fc, "fc5": fc, "fc6": fc, }, specs=[ i3.Place("fc1:out", (0.0, 0.0), angle=0.0), i3.Place("fc2:out", (0.0, -50.0), angle=0.0), i3.Place("fc3:out", (0.0, -100.0), angle=0.0), i3.Place("fc4:out", (300.0, 0.0), angle=0.0), i3.Place("fc5:out", (300.0, 100.0), angle=0.0), i3.Place("fc6:out", (300.0, 200.0), angle=0.0), i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=[ ("fc1:out", "fc4:out"), ("fc2:out", "fc5:out"), ("fc3:out", "fc6:out"), ], start_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout( # Route start_fanout to SOUTH output_direction=i3.SOUTH, # Route "fc3:out" to (20, -200) reference="fc3:out", end_position=(20, -200), ), end_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout( # Route end_fanout to SOUTH output_direction=i3.SOUTH, # Route "fc6:out" to (350, -100) reference="fc6:out", end_position=(350, -100), ), pitch=5, bend_radius=10, ), ], ) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.visualize(show=False) plt.scatter( 20, -200, marker="x", color="r", s=80, zorder=50 ) # end_position for the reference of the start_fanout plt.scatter( 350, -100, marker="x", color="r", s=80, zorder=50 ) # end_position for the reference of the end_fanout plt.show()
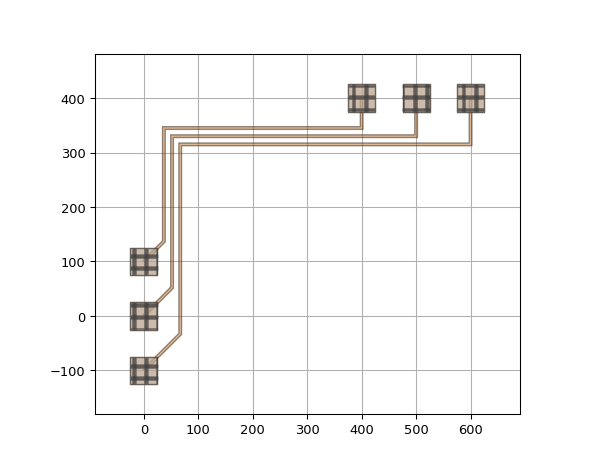
Use ManhattanFanout in electrical bundle:
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 import ipkiss3.all as i3 bp = pdk.BondPad() M1_wire_tpl = pdk.M1WireTemplate().Layout(width=5) circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={ "pad1": bp, "pad2": bp, "pad3": bp, "pad4": bp, "pad5": bp, "pad6": bp, }, specs=[ i3.Place("pad1:m1", (0.0, -100.0)), i3.Place("pad2:m1", (0.0, 0.0)), i3.Place("pad3:m1", (0.0, 100.0)), i3.Place("pad4:m1", (400.0, 400)), i3.Place("pad5:m1", (500.0, 400)), i3.Place("pad6:m1", (600.0, 400)), i3.ConnectElectricalBundle( connections=[ ("pad1:m1", "pad6:m1"), ("pad2:m1", "pad5:m1"), ("pad3:m1", "pad4:m1"), ], start_angle=45, start_straight=50, start_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout(output_direction=i3.NORTH), end_angle=-90.0, end_straight=50, end_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout(output_direction=i3.WEST), trace_template=M1_wire_tpl, pitch=15, min_gap=5, ), ], ) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.visualize()