ConnectManhattanBundle
- class ipkiss3.all.ConnectManhattanBundle
Connects multiple ports together using a bundle of waveguides separated by a fixed distance.
A Manhattan bundle consists of customizable fanouts at the start and at the end, with a Manhattan array between them.
A fanout routes inputs to evenly spaced outputs. The Manhattan array routes evenly spaced inputs to evenly spaced outputs using Manhattan routing.
- Parameters:
- end_fanout: _BundleFanout, required
The type of fanout to use at the end (if needed).
- start_fanout: _BundleFanout, required
The type of fanout to use at the start (if needed).
- cover_layers: List with type restriction, allowed types: <class ‘ipkiss.primitives.layer.Layer’>, optional
Layers used to generate additional coverage of the trace. Useful to avoid gaps between the claddings of the waveguides and DRC-errors
- control_point_reference: optional, *None allowed*
Port (instance:port identifier or an actual i3.Port) belonging to the waveguide that will be used as a reference to define the control points in the bundle. If None, use the first port defined in the list of connections.
- control_points: list, optional
Control the routing by passing through a list of
i3.H/i3.Vinstances. See also the parameter control_point_reference to identify relative to which port / waveguide the control points pass. When using i3.START, this refers to the port at the start of the bundle before the fanout.- name: ( str and String that contains only ISO/IEC 8859-1 (extended ASCII py3) or pure ASCII (py2) characters ), optional, *None allowed*
- min_spacing: float and int, float, integer, floating and number >= 0, optional
Minimal spacing between parallel sections of the route.
- end_straight: float and int, float, integer, floating and number >= 0, optional
The length of the straight end section of the route.
- start_straight: float and int, float, integer, floating and number >= 0, optional
The length of the straight start section of the route.
- min_straight: float and int, float, integer, floating and number >= 0, optional
The minimum length of any straight sections in the route.
- angle_step: float and number > 0, optional
Angle step for rounding.
- rounding_algorithm: optional
Rounding algorithm (ShapeRound, ShapeRoundAdiabaticSpline, …). Takes a shape as input and returns a new (rounded) shape.
- bend_radius: float and number > 0, optional
Bend radius for the auto-generated bends
- pitch: float and number > 0, optional
Fixed spacing between the routes. Defaults to the minimum spacing allowed by the technology.
See also
Notes
The routing uses the same algorithm as ConnectManhattan, but ensures that waveguides are routed together as an array with a given pitch. To ensure all waveguides can be routed correctly, we route the center waveguide, and we increment the bend radius with half the width of the bundle.
For the control points, only horizontal
i3.H/ verticali3.Vcontrol points can be used. Be aware that these control points are only applicable to the array section (the middle section) of the bundle. See the examples for an illustration.Currently,
i3.SBendFanoutandi3.ManhattanFanoutare the predefined fanout types that can be used for the start_fanout and end_fanout properties.Examples
Basic usage of ConnectManhattanBundle using default parameters:
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating import ipkiss3.all as i3 fc = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating() circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={ "fc1": fc, "fc2": fc, "fc3": fc, "fc4": fc, "fc5": fc, "fc6": fc, }, specs=[ i3.Place("fc1:out", (0.0, -70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc2:out", (0.0, 0.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc3:out", (0.0, 70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc4:out", (200.0, 200 - 50.0), angle=180), i3.Place("fc5:out", (200.0, 200.0), angle=180), i3.Place("fc6:out", (200.0, 200 + 50.0), angle=180), i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=[ ("fc1:out", "fc4:out"), ("fc2:out", "fc5:out"), ("fc3:out", "fc6:out"), ], start_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(), end_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(), ), ], ) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.visualize()
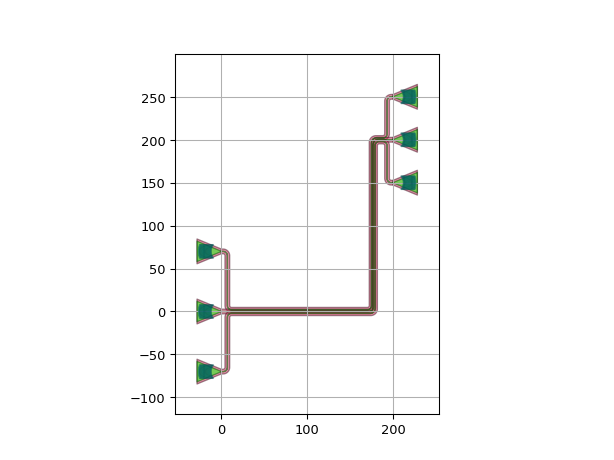
Customize the fanouts independently:
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating import ipkiss3.all as i3 fc = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating() circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={ "fc1": fc, "fc2": fc, "fc3": fc, "fc4": fc, "fc5": fc, "fc6": fc, }, specs=[ i3.Place("fc1:out", (0.0, -70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc2:out", (0.0, 0.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc3:out", (0.0, 70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc4:out", (200.0, 200 - 50.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc5:out", (200.0, 200.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc6:out", (200.0, 200 + 50.0), angle=0), i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=[ ("fc1:out", "fc6:out"), ("fc2:out", "fc5:out"), ("fc3:out", "fc4:out"), ], start_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(max_sbend_angle=80), end_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(reference="fc4:out", max_sbend_angle=70), bend_radius=10, pitch=5, ), ], ) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.visualize()
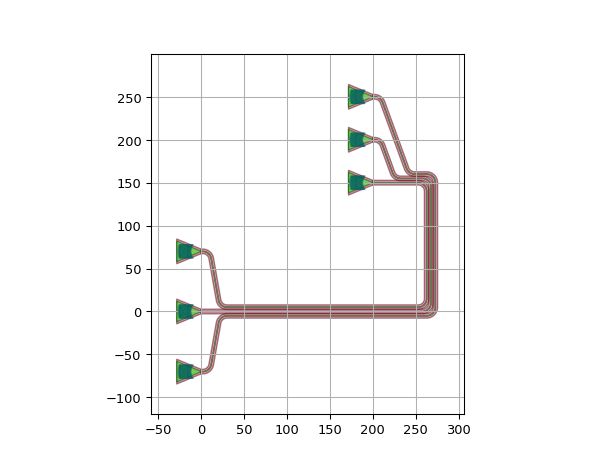
Use a different rounding algorithm for the bundle:
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating import ipkiss3.all as i3 fc = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating() circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={ "fc1": fc, "fc2": fc, "fc3": fc, "fc4": fc, "fc5": fc, "fc6": fc, "fc7": fc, "fc8": fc, "fc9": fc, "fc10": fc, }, specs=[ i3.Place("fc1:out", (0.0, -80.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc2:out", (0.0, -40.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc3:out", (0.0, 0.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc4:out", (0.0, 40.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc5:out", (0.0, 80.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc6:out", (300.0 - 100.0, 300 - 50.0), angle=-90), i3.Place("fc7:out", (300.0 - 50.0, 300.0 - 30.0), angle=-90), i3.Place("fc8:out", (300.0, 300), angle=-90), i3.Place("fc9:out", (300.0 + 50.0, 300 - 30.0), angle=-90), i3.Place("fc10:out", (300.0 + 100.0, 300 - 50.0), angle=-90), i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=[ ("fc1:out", "fc10:out"), ("fc2:out", "fc9:out"), ("fc3:out", "fc8:out"), ("fc4:out", "fc7:out"), ("fc5:out", "fc6:out"), ], start_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(max_sbend_angle=80), end_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(max_sbend_angle=80), pitch=5, rounding_algorithm=i3.EulerRoundingAlgorithm(), bend_radius=30.0, ), ], ) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.visualize()
Use the cover_layers argument to cover the bundle and fanout with additional layers:
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating import ipkiss3.all as i3 fc = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating() circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={ "fc1": fc, "fc2": fc, "fc3": fc, "fc4": fc, "fc5": fc, "fc6": fc, }, specs=[ i3.Place("fc1:out", (0.0, -70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc2:out", (0.0, 0.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc3:out", (0.0, 70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc4:out", (200.0, 200 - 50.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc5:out", (200.0, 200.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc6:out", (200.0, 200 + 50.0), angle=0), i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=[ ("fc1:out", "fc6:out"), ("fc2:out", "fc5:out"), ("fc3:out", "fc4:out"), ], start_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(), end_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(), cover_layers=[i3.TECH.PPLAYER.DOC], ), ], ) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.visualize()
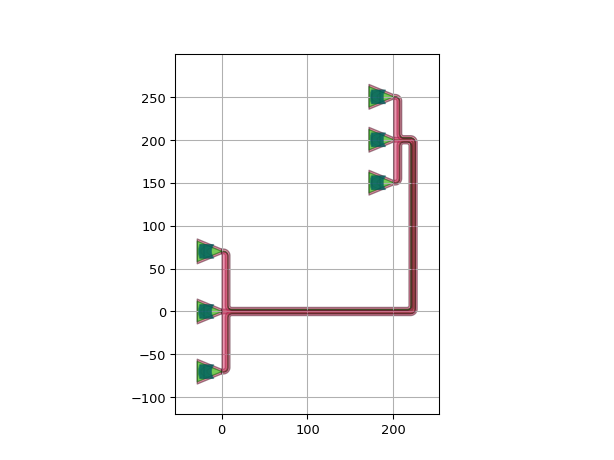
Example with strict=False in i3.Circuit (note the duplicate fc1:out connection):
"""Giving invalid connections with strict=False""" import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating import ipkiss3.all as i3 fc = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating() circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={"fc1": fc, "fc2": fc, "fc3": fc, "fc4": fc, "fc5": fc, "fc6": fc}, specs=[ i3.Place("fc1:out", (0.0, 0.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc2:out", (0.0, 40.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc3:out", (0.0, 80.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc4:out", (200.0 - 50.0, 200.0 - 30.0), angle=-90), i3.Place("fc5:out", (200.0, 200), angle=-90), i3.Place("fc6:out", (200.0 + 50.0, 200 - 30.0), angle=-90), i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=[ ("fc1:out", "fc1:out"), ("fc2:out", "fc5:out"), ("fc3:out", "fc4:out"), ], start_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(), end_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(), pitch=5, name="bundle", ), ], strict=False, name="circuit", ) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.write_gdsii("manhattan_bundle.gds") circuit_lo.visualize()
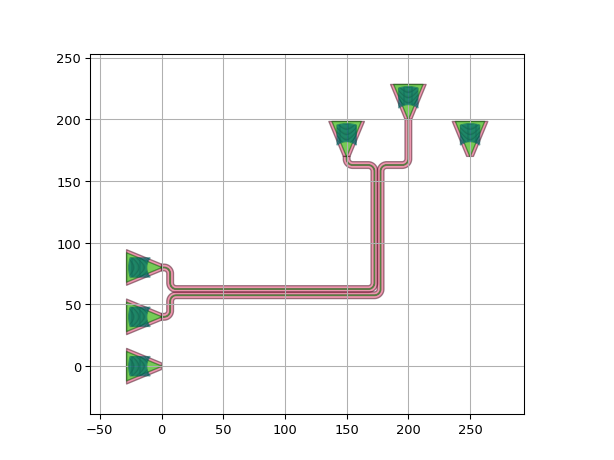
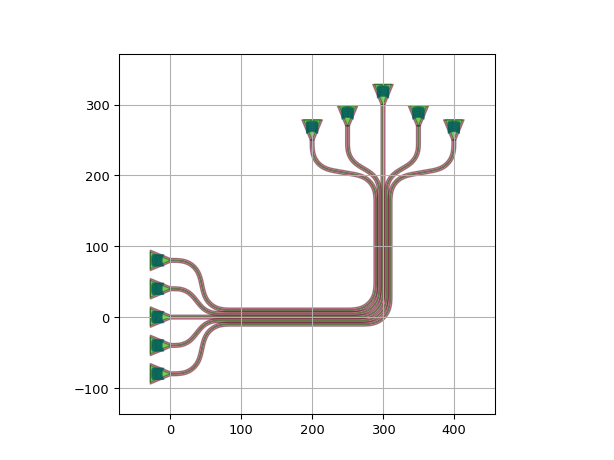
Using control points:
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating import ipkiss3.all as i3 fc = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating() circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={ "fc1": fc, "fc2": fc, "fc3": fc, "fc4": fc, "fc5": fc, "fc6": fc, }, specs=[ i3.Place("fc1:out", (0.0, -70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc2:out", (0.0, 0.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc3:out", (0.0, 70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc4:out", (200.0, 200 - 50.0), angle=180), i3.Place("fc5:out", (200.0, 200.0), angle=180), i3.Place("fc6:out", (200.0, 200 + 50.0), angle=180), i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=[("fc1:out", "fc4:out"), ("fc2:out", "fc5:out"), ("fc3:out", "fc6:out")], start_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(), end_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(), control_point_reference="fc3:out", control_points=[i3.V(i3.START + 150.0), i3.H(i3.START + 50.0), i3.V(i3.PREV - 200.0)], ), ], ) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.visualize()
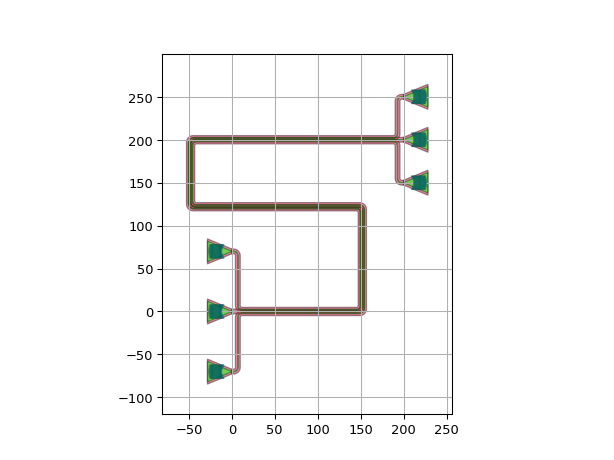
Control points are only applied to the array section. To control the fanouts, use reference and end_position:
def __example7(self): import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating import ipkiss3.all as i3 fc = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating() insts = { "fc1": fc, "fc2": fc, "fc3": fc, "fc4": fc, "fc5": fc, "fc6": fc, } place_specs = [ i3.Place("fc1:out", (0.0, -70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc2:out", (0.0, 0.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc3:out", (0.0, 70.0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc4:out", (200.0, 200 - 50.0), angle=180), i3.Place("fc5:out", (200.0, 200.0), angle=180), i3.Place("fc6:out", (200.0, 200 + 50.0), angle=180), ] route_specs = [ i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=[ ("fc1:out", "fc4:out"), ("fc2:out", "fc5:out"), ("fc3:out", "fc6:out"), ], start_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(reference="fc3:out", end_position=(50, 35), max_sbend_angle=80), end_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(reference="fc6:out", max_sbend_angle=80), control_point_reference="fc3:out", control_points=[i3.V(i3.START + 150.0), i3.H(i3.START + 50.0), i3.V(i3.PREV - 200.0)], pitch=5, min_spacing=5, ) ] circuit = i3.Circuit(insts=insts, specs=place_specs + route_specs) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.visualize()
Using different types of Fanout:
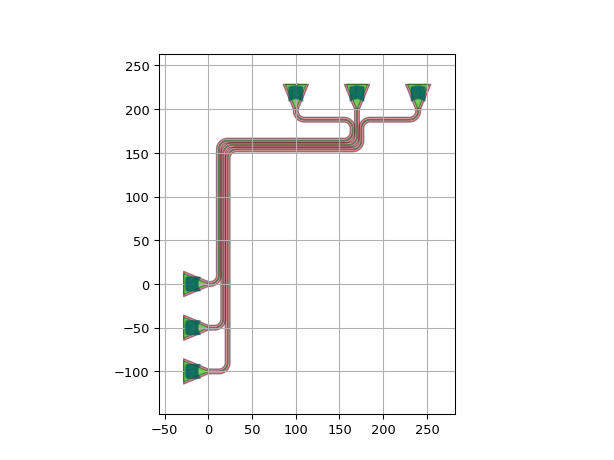
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating import ipkiss3.all as i3 fc = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating() circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={ "fc1": fc, "fc2": fc, "fc3": fc, "fc4": fc, "fc5": fc, "fc6": fc, }, specs=[ i3.Place("fc1:out", (0.0, 0), angle=0), i3.Place("fc2:out", (0, -50), angle=0), i3.Place("fc3:out", (0, -100), angle=0), i3.Place("fc4:out", (240.0, 200), angle=-90), i3.Place("fc5:out", (170.0, 200.0), angle=-90), i3.Place("fc6:out", (100.0, 200), angle=-90), i3.ConnectManhattanBundle( connections=[ ("fc1:out", "fc6:out"), ("fc2:out", "fc5:out"), ("fc3:out", "fc4:out"), ], start_fanout=i3.ManhattanFanout( output_direction=i3.NORTH, ), end_fanout=i3.SBendFanout(), pitch=5, bend_radius=10, ), ], ) circuit_lo = circuit.Layout() circuit_lo.visualize()