PCell
PCells are the core engine in IPKISS to define parametric, re-usable cells and circuits.
i3.PCellis the base type, giving complete flexibility over the parameters and views. It is used for defining atomic devices and when you need full low-level control over layout, netlist and or model views.i3.LayoutCellcan be used to create single designs by providing a list of elements to its layout view.For composing circuits,
i3.Circuitcan be used to conveniently define circuits based on instances of other cells and a set of specifications for placement and routing.
- class ipkiss3.all.PCell
PCell primitive (Parametric Cell). This class is used to describe the different aspects of a component, including the layout, netlist, compact models, hierarchy etc.
A PCell has Views and Properties. It must have a name and is member of a Library.
- Parameters:
- name: String that contains only ISO/IEC 8859-1 (extended ASCII py3) or pure ASCII (py2) characters
The unique name of the pcell
- dependencies(view=None)
return the set of dependencies (child cells) of this cell, for a given view
This works recursively: the dependencies of the view will look for their dependencies, and so on.
- Parameters:
- view: View or string
The View or name of the view from which to deduce the dependencies The default is ‘layout’
- Returns:
- set of dependencies
- get_instance(instance_name)
returns the cell corresponding to the given instance name
If there are instances in different views with this name, but corresponding to different cells, an exception will be thrown
- Returns:
- PCell object
- get_instances(instance_name=None, cell_view=None, reference_view_name=None, reference_view_type=None, owner_view_name=None, owner_view_type=None)
Queries the cell’s views for instances of other views.
If no parameters are supplied, retrieve all instances in all views A parameter will not be used if it is None.
- Parameters:
- instance_name: str
retrieve instances with the given name.
- cell_view: View or PCell
retrieve instances to the given View or PCell
- reference_view_name: str
retrieve instances to all views with the given name
- reference_view_type: View subclass
retrieve instances to all views with a given type
- owner_view_name: str
retrieve instances in the view with the given name
- owner_view_type: View subclass
retrieve instances in the views of the given type
- Returns:
- dictionary with dictionary per view: {view_name: {instance_name: instance, …}, …}
- class ipkiss3.all.LayoutCell
A PCell with an empty LayoutView,
Create a single design by instantiating i3.LayoutCell().Layout() with a list of elements.
- Parameters:
- name: String that contains only ISO/IEC 8859-1 (extended ASCII py3) or pure ASCII (py2) characters
The unique name of the pcell
Notes
unit and grid attributes are there to allow for imports/exports between GDS cells defined in technologies with different metrics
Examples
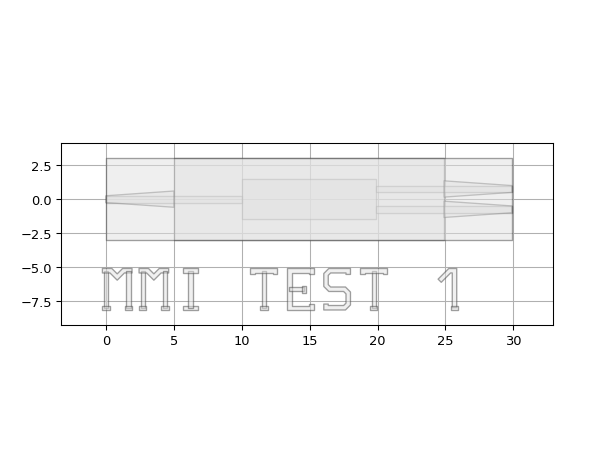
import si_fab.all as pdk import ipkiss3.all as i3 layer_wg = i3.Layer(0) layer_rib = i3.Layer(1) layer_clad = i3.Layer(2) mmi = i3.LayoutCell(name="mmi").Layout( elements=[ i3.Line(layer=layer_wg, begin_coord=(0.0, 0.0), end_coord=(10.0, 0.0), line_width=0.5), i3.Line(layer=layer_wg, begin_coord=(10.0, 0.0), end_coord=(19.9, 0.0), line_width=2.9), i3.Line(layer=layer_wg, begin_coord=(19.9, 0.75), end_coord=(29.9, 0.75), line_width=0.5), i3.Line(layer=layer_wg, begin_coord=(19.9, -0.75), end_coord=(29.9, -0.75), line_width=0.5), i3.Wedge(layer=layer_rib, begin_coord=(0.0, 0.0), end_coord=(5.0, 0.0), begin_width=0.5, end_width=1.2), i3.Line(layer=layer_rib, begin_coord=(5.0, 0.0), end_coord=(24.9, 0.0), line_width=6.0), i3.Wedge(layer=layer_rib, begin_coord=(24.9, 0.75), end_coord=(29.9, 0.75), begin_width=1.2, end_width=0.5), i3.Wedge(layer=layer_rib, begin_coord=(24.9, -0.75), end_coord=(29.9, -0.75), begin_width=1.2, end_width=0.5), i3.Line(layer=layer_clad, begin_coord=(0.0, 0.0), end_coord=(29.9, 0.0), line_width=6.0) ] ) text = i3.LayoutCell(name="text").Layout( elements=[ i3.PolygonText( layer=i3.Layer(3), text="MMI TEST 1", coordinate=(0.0, -5.0), alignment=(i3.TEXT.ALIGN.LEFT, i3.TEXT.ALIGN.TOP), font=0, height=3 ) ] ) mmi_with_text = i3.LayoutCell(name="mmi_with_text").Layout( elements=[i3.SRef(name="mmi_ref", reference=mmi), i3.SRef(name="text_ref", reference=text)] ) mmi_with_text.visualize()
Views
- class Layout
- Parameters:
- view_name: String that contains only alphanumeric characters from the ASCII set or contains _$. ASCII set is extended on PY3.
The name of the view
- class ipkiss3.all.Circuit
A PCell which derives its layout, netlist and model from a set of specifications in order to create a circuit.
Pre-defined instances of which the circuit is composed are specified as a dictionary insts. (This excludes connecting waveguides generated on the basis of the routing specifications).
Placement and routing is done with
i3.place_and_routeusing a combination of place_specs and route_specs (specifications as in Placement and Routing Reference).Ports are exposed using
i3.expose_portsusing port_specsThe netlist and circuit model views are derived from the layout using netlist extraction.
Create a single design by instantiating i3.Circuit directly, or create a parametric circuit by inheriting from it.
- Parameters:
- strict:
If True, any error will raise an exception and stop the program flow. If False, any routing error will give a warning and draw a straight line on an error layer. See
i3.ConnectLogicalfor more information.- exposed_ports: ( dict ), *None allowed*
Ports to be exposed, mapping {‘instance_name:port_name’: external_port_name’} map for i3.expose_ports().Set to None (default) to expose all unconnected ports
- specs: list
Placement and routing specifications
- insts: OrderedDict and key: str, value: PCell, _View
Instances of child cells which this circuit is composed of: {‘instance_name’: cell, …} where cell is an i3.PCell object.
- name: String that contains only ISO/IEC 8859-1 (extended ASCII py3) or pure ASCII (py2) characters
The unique name of the pcell
Warning
The insts property of Circuit contains the instances specified by the user, while the instances property of the Layout view contains the full set of instances including connecting waveguides.
Notes
The following 2 are largely equivalent (you can also navigate to i3.Circuit in your code editor to see the exact behavior):
class MyCircuit(i3.Circuit): def _default_insts(self): return my_instances def _default_specs(self): return my_specs def _default_exposed_ports(self): return my_exposed_ports class MyCircuit(i3.PCell): class Layout(i3.LayoutView): def generate(self, layout): layout += i3.place_and_route(my_instances, specs) layout += i3.expose_ports(layout, my_exposed_ports) return layout class Netlist(i3.NetlistFromLayout): pass class CircuitModel(i3.CircuitModelView): def _generate_model(self): return HierarchicalModel.from_netlistview(self.netlist_view)
Circuitprovides a convenient standardized workflow for creating specification-based layout-driven circuits. When more flexibility is needed, inherit from i3.PCell instead. Changing from i3.Circuit to i3.PCell is done as in the example above.Examples
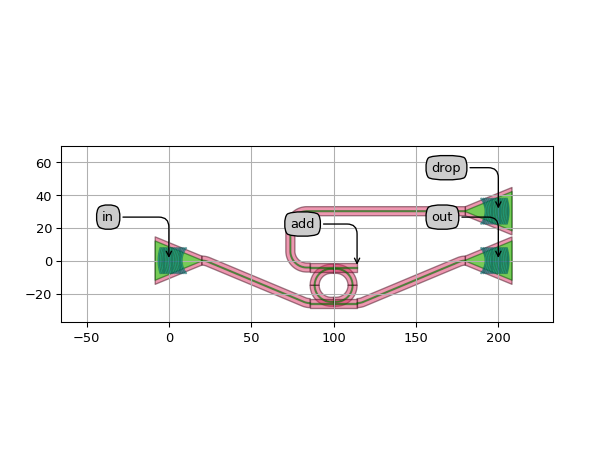
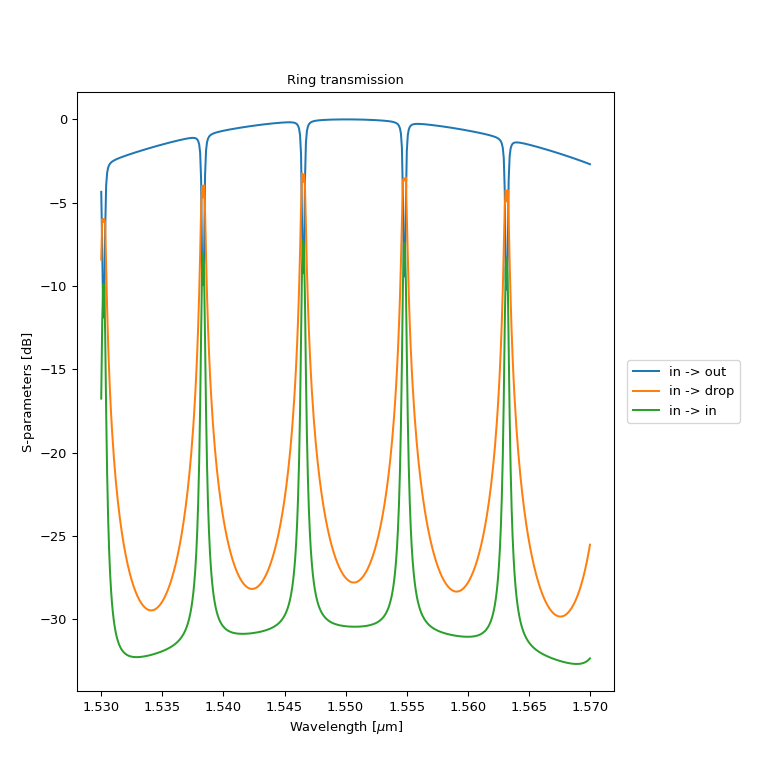
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 import ipkiss3.all as i3 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating from picazzo3.filters.ring import RingRect180DropFilter import numpy as np # waveguide template waveguide_template = pdk.SiWireWaveguideTemplate() waveguide_template.Layout(core_width=0.5, cladding_width=5.5) # instances fibcoup = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating(start_trace_template=waveguide_template) coupler_parameters = dict( cross_coupling1=1j * 0.0784**0.5, straight_coupling1=0.9216**0.5, reflection_in1=1j * 0.030 ) ring = RingRect180DropFilter( ring_trace_template=waveguide_template, coupler_trace_templates=[waveguide_template, waveguide_template] ) ring.Layout(bend_radius=10.0, straights=[3.0, 0.0], coupler_spacings=[0.8, 0.8]) ring.CircuitModel(coupler_parameters=[coupler_parameters, coupler_parameters]) fc_spacing = 200.0 ring_test_site = i3.Circuit( insts={"fc_in": fibcoup, "ring": ring, "fc_out": fibcoup, "fc_drop": fibcoup}, specs=[ i3.Place("fc_in:vertical_in", (0.0, 0.0)), i3.Place("fc_out:vertical_in", (fc_spacing, 0.0)), i3.FlipH("fc_out"), i3.Place("fc_drop:vertical_in", (fc_spacing, 30.0)), i3.FlipH("fc_drop"), i3.Place("ring", (0.5 * fc_spacing, -15.0)), i3.ConnectBend([("fc_in:out", "ring:in1"), ("fc_out:out", "ring:out1")], bend_radius=10), i3.ConnectManhattan("fc_drop:out", "ring:out2", bend_radius=10), ], exposed_ports={ "fc_in:vertical_in": "in", "fc_out:vertical_in": "out", "fc_drop:vertical_in": "drop", "ring:in2": "add", }, ) ring_test_layout = ring_test_site.Layout() ring_test_layout.visualize(annotate=True) sim_wavelengths = np.linspace(1.53, 1.57, 500) ring_cm = ring_test_site.CircuitModel() s_mat = ring_cm.get_smatrix(sim_wavelengths) s_mat.visualize(term_pairs=[("in", "out"), ("in", "drop"), ("in", "in")], scale="dB", title="Ring transmission")
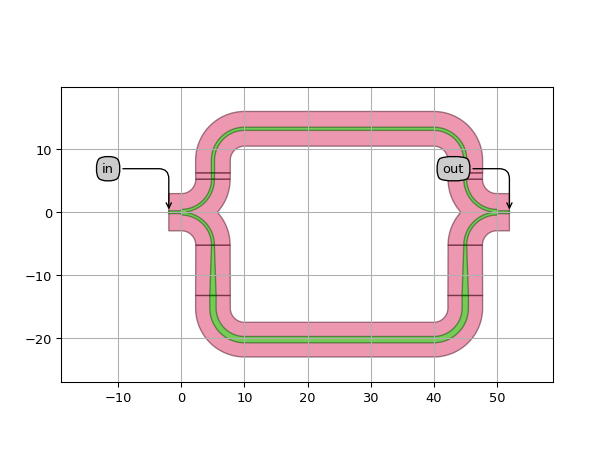
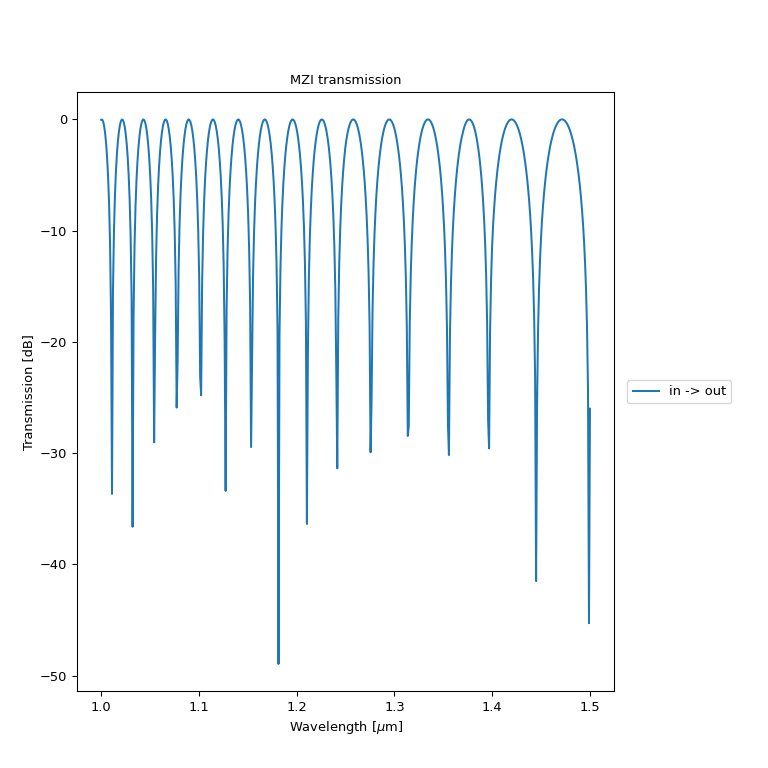
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 import ipkiss3.all as i3 import numpy as np from picazzo3.wg.splitters import WgYSplitter, WgYCombiner # waveguide templates for MZI arms wg_t_arm1 = pdk.SiWireWaveguideTemplate() wg_t_arm1.Layout(core_width=1.0, cladding_width=5.5) wg_t_arm2 = pdk.SiWireWaveguideTemplate() wg_t_arm2.Layout(core_width=0.5, cladding_width=5.5) mzi = i3.Circuit( insts={"splitter": WgYSplitter(), "combiner": WgYCombiner()}, specs=[ i3.Place("splitter", (0, 0)), i3.Place("combiner", (50, 0), relative_to="splitter"), i3.ConnectManhattan("splitter:arm1", "combiner:arm1", "arm1", trace_template=wg_t_arm1), i3.ConnectManhattan("splitter:arm2", "combiner:arm2", "arm2", trace_template=wg_t_arm2), ], exposed_ports={ "splitter:center": "in", "combiner:center": "out", }, ) mzi_layout = mzi.Layout() mzi_layout.visualize(annotate=True) sim_wavelengths = np.linspace(1.0, 1.5, 500) mzi_cm = mzi.CircuitModel() s_mat = mzi_cm.get_smatrix(sim_wavelengths) s_mat.visualize(term_pairs=[("in", "out")], scale="dB", title="MZI transmission", ylabel="Transmission [dB]")
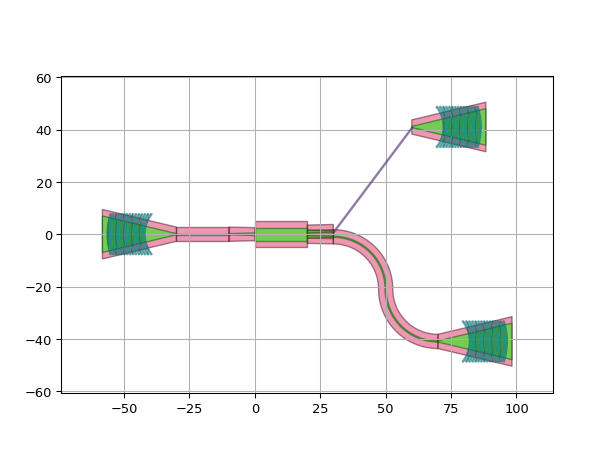
import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 from ipkiss3 import all as i3 from picazzo3.fibcoup.curved import FiberCouplerCurvedGrating from picazzo3.filters.mmi.cell import MMI1x2Tapered # Create the template for the MMI mmi_trace_template = pdk.SiWireWaveguideTemplate() mmi_trace_template.Layout(core_width=5.0, cladding_width=10.0) mmi_access_template = pdk.SiWireWaveguideTemplate() mmi_access_template.Layout(core_width=1.0, cladding_width=5.0) mmi = MMI1x2Tapered( mmi_trace_template=mmi_trace_template, input_trace_template=mmi_access_template, output_trace_template=mmi_access_template, trace_template=i3.TECH.PCELLS.WG.DEFAULT, ) mmi.Layout(transition_length=10.0, length=20.0, trace_spacing=2.0) # Create the template for the grating couplers end_wg_tmpl = pdk.SiWireWaveguideTemplate() end_wg_tmpl.Layout(core_width=10.0, cladding_width=2 * i3.TECH.WG.TRENCH_WIDTH + 10.0) coupler = FiberCouplerCurvedGrating( start_trace_template=i3.TECH.PCELLS.WG.DEFAULT, wide_trace_template=end_wg_tmpl ) coupler.Layout(period_x=1.0, focal_distance_x=20.0) # Place and route the MMI and grating couplers circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={"coupler_in": coupler, "coupler_out1": coupler, "coupler_out2": coupler, "mmi": mmi}, specs=[ i3.Place("mmi", (0, 0)), i3.Place("coupler_in", (-50, 0), relative_to="mmi"), i3.Place("coupler_out1:out", (40, -40), relative_to="mmi:out1"), # Place ports too close together for bend_radius=20: i3.Place("coupler_out2:out", (30, 40), relative_to="mmi:out2"), i3.FlipH(["coupler_out1", "coupler_out2"]), i3.ConnectBend( [("coupler_in:out", "mmi:in"), ("mmi:out1", "coupler_out1:out"), ("mmi:out2", "coupler_out2:out")], bend_radius=20, ), ], strict=False, # Will draw a straight line on an error layer ) lv = circuit.get_default_view(i3.LayoutView) lv.visualize()
i3.place_and_route and i3.Circuit can also be used to place and route electrical components:
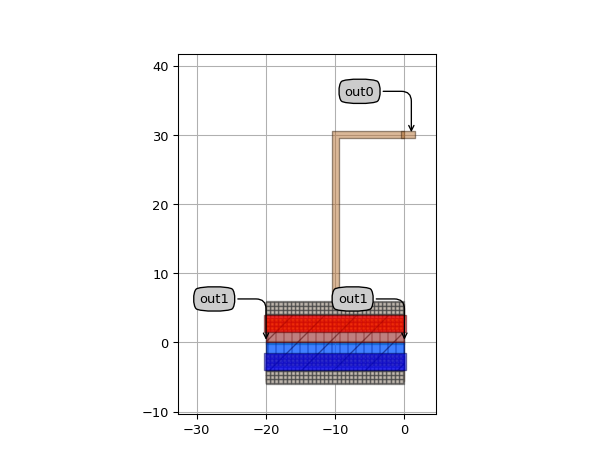
"""An important requirement when using i3.Circuit and i3.place_and_route is that the ports should have an angle. For optical ports, this will always be the case. For electrical ports, however, the angle is not always specified. In this example, we'll extend ElectricalWire and PhaseShifterWaveguide to specify the angles on its electrical ports. We'll also make sure the metal layers match as this is required by ConnectElectrical if no VIAs are used. """ import si_fab.all as pdk # noqa: F401 import ipkiss3.all as i3 layer = pdk.PhaseShifterWaveguide().Layout().ports["in"].layer class ElectricalWire(i3.ElectricalWire): class Layout(i3.ElectricalWire.Layout): def _generate_ports(self, ports): ports = super(ElectricalWire.Layout, self)._generate_ports(ports) angles = self.shape.angles_deg() in_angle, out_angle = angles[0] + 180, angles[-1] ports["in"].angle = in_angle ports["out"].angle = out_angle ports["in"].layer = layer ports["out"].layer = layer return ports class PhaseModulator(pdk.PhaseShifterWaveguide): class Layout(pdk.PhaseShifterWaveguide.Layout): def _generate_ports(self, ports): ports = super(PhaseModulator.Layout, self)._generate_ports(ports) ports["anode"].angle = 90 ports["cathode"].angle = -90 ports["anode"].layer = layer ports["cathode"].layer = layer return ports wire = ElectricalWire() phmod = PhaseModulator() phmod.Layout(length=20) circuit = i3.Circuit( insts={"wire": wire, "modulator": phmod}, specs=[ i3.Place("modulator:out", (0, 0)), i3.Place("wire:in", (0, 30)), i3.ConnectElectrical("modulator:anode", "wire:in"), ], exposed_ports={ "wire:out": "out0", "modulator:out": "out1", "modulator:in": "in1", }, ) lay = circuit.Layout() lay.visualize(annotate=True)
Views
- class Layout
- Parameters:
- view_name: String that contains only alphanumeric characters from the ASCII set or contains _$. ASCII set is extended on PY3.
The name of the view
- class Netlist
- Parameters:
- view_name: String that contains only alphanumeric characters from the ASCII set or contains _$. ASCII set is extended on PY3.
The name of the view
- Other Parameters:
- layout_view: _LayoutView, locked
Layout view on which this netlist is based
- class CircuitModel
- Parameters:
- layout_view: ( _LayoutView ), *None allowed*
- netlist_view: ( NetlistView ), *None allowed*
- view_name: String that contains only alphanumeric characters from the ASCII set or contains _$. ASCII set is extended on PY3.
The name of the view
- Other Parameters:
- solver: str and String that contains only ISO/IEC 8859-1 (extended ASCII py3) or pure ASCII (py2) characters, locked
circuit solver to use