camfr_mode_fields
- ipkiss3.all.device_sim.camfr_mode_fields(material_stack, wavelengths, modes=None, components=None, sample_dist=0.01)
Calculates the fields for the modes for a material stack using the camfr mode solver.
This function can be useful to get insight in camfr_guided_modes, as the latter only returns the calculated neffs.
- Parameters:
- material_stack: MaterialStack object
The stack of ipkiss materials to calculate the modes for.
- wavelengths: array_like
An array of wavelengths to calculate the modes for
- modes: List[str]
A list of modenames to calculate the fields for. [‘TE0’, ‘TM1’] will select the zeroth order TE mode and the first order TM mode
- components: List[str]
A list of field components to calculate. [‘E1’, ‘E2’, ‘Ez’] will calculate all E fields
- sample_dist: float
Distance between the positions to sample the fields on.
- Returns:
- tuple
Tuple of fields and x_positions. fields is a numpy array of size (n_modes, n_wavelengths, n_components, n_x_positions) and of type np.complex128, while x_positions is an array of coordinates at which the field is sampled
Examples
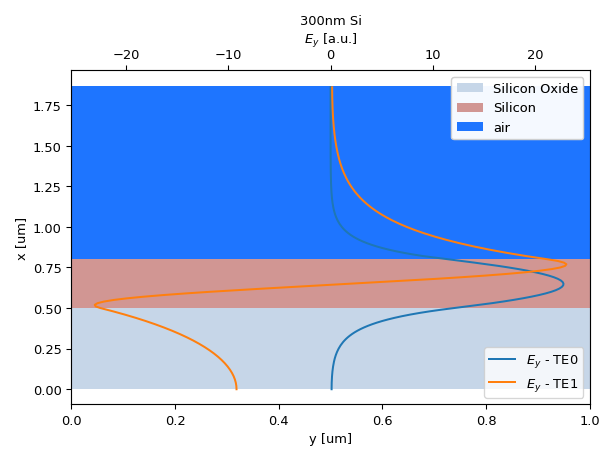
import si_fab.all as pdk from pysics.basics.material.material_stack import MaterialStack import ipkiss3.all as i3 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # we define a MaterialStack mstack = MaterialStack( name="300nm Si", materials_heights=[ (i3.TECH.MATERIALS.SILICON_OXIDE, 0.500), (i3.TECH.MATERIALS.SILICON, 0.300), (i3.TECH.MATERIALS.AIR, 1.070) ] ) wavelengths = np.linspace(1.54, 1.56, 10) # calculate the fields fields, positions = i3.device_sim.camfr_mode_fields( mstack, wavelengths, modes=['TE0', 'TE1'], components=['E2', 'H2'], sample_dist=0.010 ) # we select the fields for a certain mode and # a certain wavelength TE0 = fields[0, 0, 0, :].real TE1 = fields[1, 0, 0, :].real max_fields = max(np.max(TE0), np.max(TE1)) min_fields = min(np.min(TE0), np.min(TE1)) fig = mstack.visualize(show=False, titlepad=35) ax1 = fig.gca() ax1.set_ylabel('x [um]') ax1.set_xlabel('y [um]') ax2 = ax1.twiny() ax2.set_xlabel(r'$E_y$ [a.u.]') ax2.plot(TE0, positions, label='$E_y$ - TE0') ax2.plot(TE1, positions, label='$E_y$ - TE1') # we add a legend plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.tight_layout() plt.show()